-
Faculty of Arts and HumanitiesDean's Office, Faculty of Arts and HumanitiesJakobi 2, r 116-121 51005 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0Institute of History and ArchaeologyJakobi 2 51005 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0Institute of Estonian and General LinguisticsJakobi 2, IV korrus 51005 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0Institute of Philosophy and SemioticsJakobi 2, III korrus, ruumid 302-337 51005 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0Institute of Cultural ResearchÜlikooli 16 51003 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0Institute of Foreign Languages and CulturesLossi 3 51003 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0School of Theology and Religious StudiesÜlikooli 18 50090 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0Viljandi Culture AcademyPosti 1 71004 Viljandi linn, Viljandimaa EST0Professors emeriti, Faculty of Arts and Humanities0Associate Professors emeriti, Faculty of Arts and Humanities0Faculty of Social SciencesDean's Office, Faculty of Social SciencesLossi 36 51003 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0Institute of EducationJakobi 5 51005 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0Johan Skytte Institute of Political StudiesLossi 36, ruum 301 51003 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0School of Economics and Business AdministrationNarva mnt 18 51009 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0Institute of PsychologyNäituse 2 50409 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0School of LawNäituse 20 - 324 50409 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0Institute of Social StudiesLossi 36 51003 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0Narva CollegeRaekoja plats 2 20307 Narva linn, Ida-Virumaa EST0Pärnu CollegeRingi 35 80012 Pärnu linn, Pärnu linn, Pärnumaa EST0Professors emeriti, Faculty of Social Sciences0Associate Professors emeriti, Faculty of Social Sciences0Faculty of MedicineDean's Office, Faculty of MedicineRavila 19 50411 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa ESTInstitute of Biomedicine and Translational MedicineBiomeedikum, Ravila 19 50411 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa ESTInstitute of PharmacyNooruse 1 50411 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa ESTInstitute of DentistryL. Puusepa 1a 50406 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa ESTInstitute of Clinical MedicineL. Puusepa 8 50406 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa ESTInstitute of Family Medicine and Public HealthRavila 19 50411 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa ESTInstitute of Sport Sciences and PhysiotherapyUjula 4 51008 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa ESTProfessors emeriti, Faculty of Medicine0Associate Professors emeriti, Faculty of Medicine0Faculty of Science and TechnologyDean's Office, Faculty of Science and TechnologyVanemuise 46 - 208 51003 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa ESTInstitute of Computer ScienceNarva mnt 18 51009 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa ESTInstitute of GenomicsRiia 23b/2 51010 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa ESTEstonian Marine Institute0Institute of PhysicsInstitute of ChemistryRavila 14a 50411 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0Institute of Mathematics and StatisticsNarva mnt 18 51009 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0Institute of Molecular and Cell BiologyRiia 23, 23b - 134 51010 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa ESTTartu ObservatoryObservatooriumi 1 61602 Tõravere alevik, Nõo vald, Tartumaa EST0Institute of TechnologyNooruse 1 50411 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa ESTInstitute of Ecology and Earth SciencesJ. Liivi tn 2 50409 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa ESTProfessors emeriti, Faculty of Science and Technology0Associate Professors emeriti, Faculty of Science and Technology0Institute of BioengineeringArea of Academic SecretaryHuman Resources OfficeUppsala 6, Lossi 36 51003 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0Area of Head of FinanceFinance Office0Area of Director of AdministrationInformation Technology Office0Administrative OfficeÜlikooli 17 (III korrus) 51005 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0Estates Office0Marketing and Communication OfficeÜlikooli 18, ruumid 102, 104, 209, 210 50090 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0Area of Vice Rector for DevelopmentCentre for Entrepreneurship and InnovationNarva mnt 18 51009 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0University of Tartu Natural History Museum and Botanical GardenVanemuise 46 51003 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0International Cooperation and Protocol Office0University of Tartu MuseumLossi 25 51003 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0Area of RectorRector's Strategy OfficeInternal Audit OfficeArea of Vice Rector for Academic AffairsOffice of Academic Affairs0University of Tartu Youth AcademyUppsala 10 51003 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0Student Union OfficeÜlikooli 18b 51005 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0Centre for Learning and TeachingArea of Vice Rector for ResearchUniversity of Tartu LibraryW. Struve 1 50091 Tartu linn, Tartu linn, Tartumaa EST0Grant Office
University of Tartu researcher receives prestigious ERC Starting Grant to study the arms race between bacteria and viruses
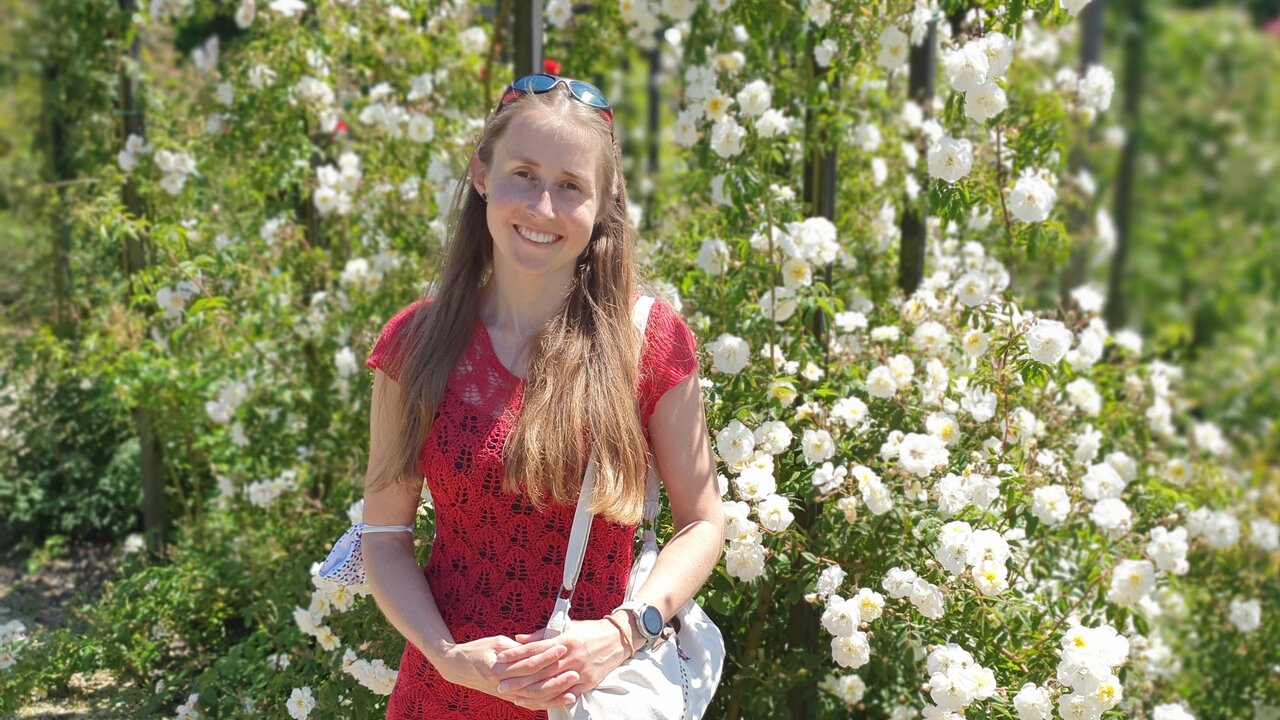

The two-way defence mechanisms of bacteria and phages, viruses of the bacteria, can offer a solution to antibiotic resistance problems. Hedvig Tamman, Associate Professor of Genetics at the Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology, University of Tartu, received the Starting Grant from the European Research Council (ERC) to study the microbial arms race.
Antibiotic resistance is a growing problem in the treatment of infectious diseases caused by bacteria. Bacteria-attacking viruses can offer new solutions, for example, for developing antibiotics and their additives. The prospect of using phages in the fight against pathogenic bacteria has long been recognised, but their very high specificity and unpredictable reproduction have limited their wider use in medicine.

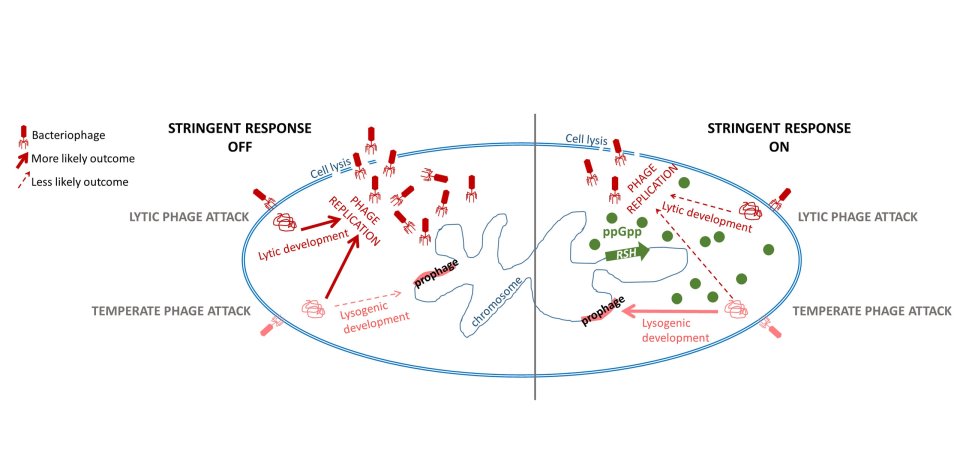
Tamman’s study bridges several gaps in the research on bacteria, phages and their interaction. “As bacteria and phages have co-evolved since the beginning of time, there is a kind of arms race between them – phages develop a mechanism to overcome all the bacterial defence systems,” said Tamman.
On the one hand, the researcher studies how bacteria defend themselves against phages. For example, bacteria have defence mechanisms against phages and other stressors, such as the toxin-antitoxin system in chromosomes and the stringent response – the latter puts the bacterium, when stressed, into a kind of hibernation. This helps it survive the antibiotic attack and supports the development and spread of resistance. On the other hand, Tamman hopes to discover what helps the phages paralyse the bacterial stringent response.
"Although the bacterium Pseudomonas putida that I study is not medically important, it is related to human and plant pathogens. Knowing how phages fight this bacterium gives us ideas that could help us fight bacterial diseases in the future."
The ERC Starting Grant for early-stage researchers is €1.5 million over five years. The project “Deciphering stringent response proteins and toxin-antitoxin systems in the arms race between bacteria and phages” (abbreviation PhaBacArms) starts at the beginning of 2024 and runs until the end of 2028.
Hedvig Tamman defended her PhD in genetics at the University of Tartu in 2016. Her doctoral thesis dealt with the functionality of chromosomal toxin-antitoxin systems of the bacterium Pseudomonas putida. From 2016 to 2021, Tamman was a postdoctoral researcher at the Free University of Brussels, where she worked on determining bacterial stress responses and the structure of proteins involved in these responses.
It’s viruses all the way down: a conversation with Hsiao-Han Chang, Gytis Dudas, and Hedvig Tamman 30.10.23 (EMBO podcast)
Article in Estonian newspaper Postimees 05.09.2023 (in Estonian)
Radio interview with Hedvig Tamman on the radio show Kukkuv õun 5.09.2023 (in Estonian)
Earlier news article about the Hedvig Tamman's EMBO Installation Grant
IMCB's blog about Hedvig Tamman and her postdoc years (in Estonian)
Read more similar news